Would you like to start a conversation with other industry leaders to brainstorm a challenge or to just know more on a particular topic?
Engage in online discussions with your Peers
Start NowEditor’s Note
Change and growth of Technology has always been of interest to us humans, as has been the single largest source of transformation of our lives. The advent of Shared Services, GICs and BPM companies, for instance, are a clear result of the advancing technologies which have created dramatic changes in business processes as well as in infrastructure.
The cutting edge levels of technology are being rapidly absorbed by companies for their own benefits as well as that of their customers. Shared Services, GICs and BPM companies should look outside and beyond their internal company or clients and experience how technology is changing the life of the ultimate customers. It is now time to create a structured ‘outside-in’ knowledge blueprint to remain relevant. Progressive Shared Services, GICs could do well to leverage the innovation power of technology to make a difference to their parent company or client business.
India’s Bombay Stock Exchange, established in 1875, was Asia’s first securities exchange where brokers would meet and transact under a tree. Indian capital markets have evolved significantly and come a long way since then.
India is now an active hunting ground for global traders and foreign institutions due to the relative stability of earnings of Indian firms compared to Asian peers, the dominance of domestic consumption in the economy, relatively lower correlation with global markets, and the diversity of its equity market. Even within the country, the capital markets present an attractive opportunity for traders, market makers, and hedge funds. Indian exchanges rank amongst the top exchanges globally in terms of number of contracts traded across equity, equity derivatives, and index derivatives segments.
Competition amongst exchanges has also intensified. Technology infrastructure across exchanges is continuously being upgraded and trading costs have come down significantly.
A New Age Trading Format on the Bourses
There are now several opportunities for applying algorithmic and high frequency trading strategies in India. Algorithmic trading, as the name suggests, is a computer trading program that automatically submits trades to an exchange without any human intervention.
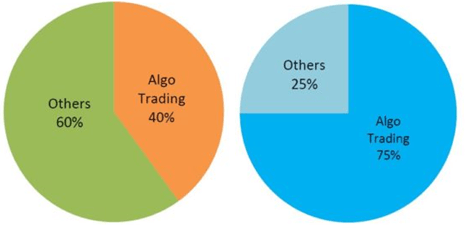
SEBI permitted algorithmic trading in 2008, and market maturity has grown manifold since then. Electronic trading now comprises more than 60% of total market volumes.
SEBI has supported the need for greater technological sophistication and is now expanding the scope of participation by bringing in more participants under its regulatory ambit. It is closely watching the growth in the algorithmic trading space and continues to evolve risk-management and market framework guidelines for algorithmic trading in consultation with market participants.
There are about 1750 securities traded on Indian exchanges and over 350 of them are liquid and actively traded. In a developing market such as India, there are several market variations which results in higher bid-ask and arbitrage spreads.
Algorithmic trading is a computer trading program that automatically submits trades to an exchange without any human intervention.
These spreads were maintained by manual brokers, but now algo based market makers can maintain tighter spreads at a lower cost. High volumes, volatility and attractive spreads have therefore made algo trading an attractive proposition. Recognizing the benefits of algorithmic trading, SEBI and NSE/ BSE offered direct market access in India in August 2008.
There was some skepticism initially, however, market participants saw the benefit of the improved infrastructure and the share of non-algorithmic trading has declined to ~40% since then.
The Indian market has evolved rapidly over the past decade and increasing sophistication amongst players, regulators, customers, and exchanges has paved the way for market-wide adoption of latest technology and an increase in market depth, breadth, and efficiency. SEBI has over the years provided the requisite push for greater technological adoption.
The automation of trading and post trading systems on major stock exchanges ensured that investors paid less in trading spreads for their trades and fundamentally altered the economics of the business of stock exchanges. Driven by the growing prevalence of electronic trading, there has been market-wide adoption of improved technology across the value chain.
Over the last three years, there has been ~50% improvement in data and speed of execution, through availability of tick-by-tick data, improved market depth, and availability of cleaned data for back-testing. All the exchanges have been continuously investing in technology. NSE has implemented horizontal scalability to handle 10 times the current order flow.
Latency has been minimized significantly, and the system can handle 2 billion order messages per second. BSE has implemented one of the fastest and highest throughput system in the world.
Tapping the Opportunity
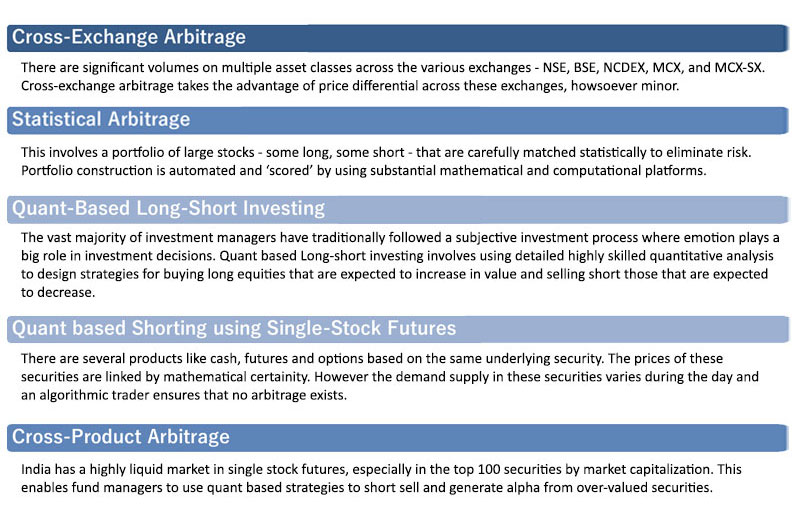
The Indian market microstructure along with the conducive trading environment throws open several opportunities in arbitrage space, such as:
Evolution of Algo Trading Companies
The past few years have seen the rise of algorithmic trading companies all over the world. Some of the best performing hedge funds attribute their success to it. Devoid of human emotions, repelling latency, technology-oriented and fast-paced, algorithmic trading executes trading commands instantly and with accuracy.
The requirement of infrastructure and super specialization, both in technology as well as modern investment strategies has ensured that trade decisions have moved from single individuals to the tech systems.
Business Case for Trading Companies
At its core, the business is nothing more than automating trading strategies. Liquidity providers, jobbers, arbitragers have all been present since stock exchanges have been present. In the current scenario, all these functions and strategies are being automated and then optimized. The battle in the 'pits' has moved to high end servers and low latency links but the core objective remains the same. For the traders and trading firms, the business case moves from low volume, high margin case to very high volume, low margin.
Strangely, in many instances there may be no “customer” of the business. A majority of trading is done with proprietary capital - so the risk and reward lies solely with the company itself. In such a situation, the “customer” at best, could be the propriety fund holder, who could well be the CEO of the trading house. However conceptually, Algo, or High Frequency Trading need not be restricted to propriety funds. The same could well be applied to a traditional model of trading on behalf of an individual (or organization) for a fee.
The entire business case is based on the accuracy of prediction of market movements, as computed by propriety systems using very sophisticated strategies. Hence the “suppliers” to this business line, in most cases, would be the providers of technology applications, trading strategy experts, and data providers (the exchanges). In several cases, experts design their own strategies as well as their own trading applications.
As the prevalence and popularity of Algo trading has grown in India, most commercial brokers offer access to connect via an “API” to their customers at very low or no fees. Sophisticated traders can use these APIs and develop their strategies to automatically send orders to the exchange, hence building an algo trading system from their homes.
As is obvious, the use of high-end technology is critical to this business. Artificial Intelligence and machine learning are used to develop smarter strategies to trade more profitably. Some of the popular trading applications/APIs used in India are Omnesys Nest, Presto ATS, ODIN, AlgoNomics, MetaTrader and Estee.
Work-flow/ Indicators/ Challenges/ Risks
In a professional automated setup, most work flows are also automated. A simple standard work flow is given in the table below:

Rogue Trading Prevention Methodologies
Rogue trading in this scenario involves the Strategy sending message which causes unintended consequences. Though the risk layer is meant to catch these sorts of issues, however, sometimes either the risk layer is not designed appropriately to prevent these issues or is not implemented/ controlled appropriately. This leads to runaway trading scenarios sometime resulting in flash crashes as well. This is always harmful for the company in question and sometimes for the market in general as well.
Since this format of trading is completely driven by systems, an internal risk from employees themselves carrying out trades for their personal benefits or other intentional malpractices is low. However, as in all prop trading firms, each employee is required to submit details of all trades they have conducted in the stock exchanges and are also required to take prior permission if they trade on individual stocks (other than possibly indices or mutual funds). Such restrictions are even tighter in case the firm is involved in market research as well.
Certain unethical practices such as ‘front running’ have happened since forever. In this case the traders themselves attempt to trade before the price changes based on an actual order is placed by their client.

These practices can happen even in an Algo trading setup. However all over the world such practices are now illegal and companies put in place strict measures to prevent this.
Data Security
Strategy code and logic is highly valuable IP for any company.
Even information on trades and trading activity is guarded closely. This is primarily done through high-end firewalls and role based access systems.

Special Skills
The need for specialized skills for running such companies successfully could well depend upon the type of strategies followed by them. For instance for firms largely following high frequency trading, strategies or trading logic is relatively straight forward and known to all.
However, the differentiating factor is execution of this strategy. Hence, technical coding skills are key – Most HFT firms would be present on Day 1 at IIT. On the other hand, firms that are Non HFT/ Non-Market Neutral trading strategies require a very different skill set. This requires a unique logic towards trading - through research/ analysis of market movements/ order book etc. - and here execution is relatively straight forward. Typically such firms hire laterally from the existing pool of traders having deep analytical skills to carry out the intensive research required.
What Next?
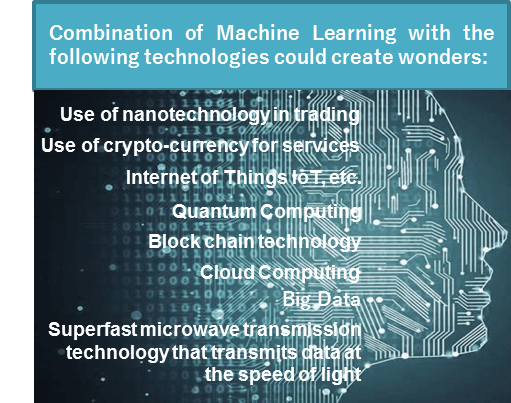
India is slightly on the back foot in the cutting edge world of algo trading. The more developed markets are successfully experimenting on both increasing depth and width of trading. Applications employing Machine Learning carry out multiple transactions per second and continuously improve themselves by analysing data. This form of ‘learning’ further refines the strategy allowing more options for finer levels of trade. On the other hand latency is being tapped and crunched even more. The use of Microwaves to transfer data has begun to show very positive trends
Transactions now happen not merely over micro seconds, but over nano seconds. Instead of a few hundred or thousand transactions (orders) a second, machines have now graduated to generate thousands of orders in a millisecond.

A transformational Innovation
The industry has globally and in India been a very successful contributor for the tremendous rise in market liquidity and also huge drop in impact cost, which is also a measure of cost that a buyer or seller has to incur due to the sheer lack of liquidity of any particular stock. There is no doubt that this industry has now become the norm rather than the exception by the use of computer technology, which has been nothing short of transformational. Trading at the micro level has dramatically changed the way the traditionalists thought. Weeding out inefficiencies in markets is a very important next step in a robust and stable market, which is what this industry practice does. This leads to accurate price discovery and very tight bid/ ask spreads which in turn enable and give confidence to various traders to trade in the markets. This in-turn increases market depth and reach, hence improving liquidity and reducing risk.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

Sandeep Tyagi is a quant and algorithms expert and serial entrepreneur, who has started and successfully scaled several profitable businesses. He was the founder and CEO of Inductis, a consulting and analytics firm that he scaled up and subsequently sold to EXL Service. He is also a board member of the YPO and a recipient of the 40 under 40 award from New Jersey. He is a B. Tech. from IIT Delhi and an MBA from Columbia Business School. He also holds a Certificate in Quantitative Finance (CQF).
Sandeep is the Chairman of Estee Advisors Pvt Ltd, a quant-based investment management and execution and services provider. Estee is a pioneer in building algorithmic investment products and has a strong track record as an investment manager and trade execution services provider in Indian capital markets. Estee is a SEBI-registered Portfolio Manager Service (PMS) provider and a registered broker-member with all the major Indian exchanges.




